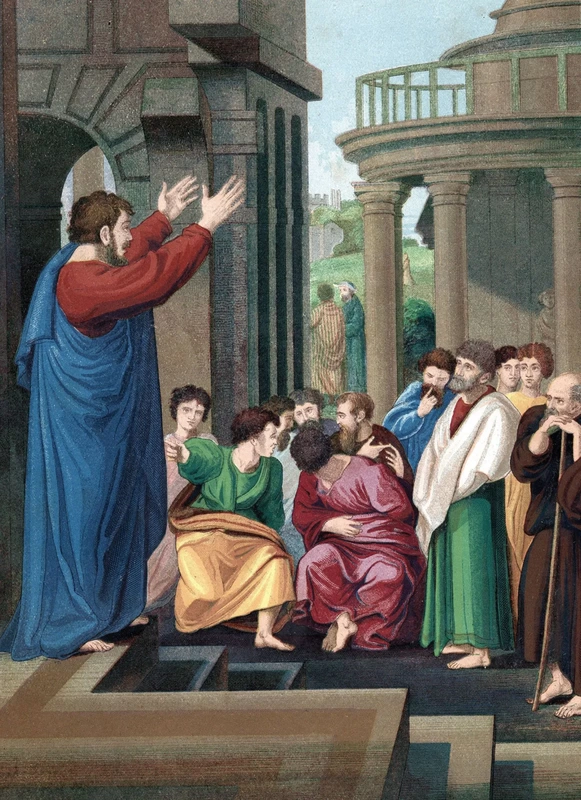
In Romans 11:11–24 Paul compares Israel to the natural branches of a cultivated olive tree and the Gentile believers to the branches of a wild olive tree. The natural branches (Israel) were broken off, and the wild branches (Gentiles) were grafted in (verse 17). The Gentiles, then, have been made partakers of the promises and inherit the blessings of God’s salvation.
It is important to understand how God called Israel to be His people and how they failed to fulfill that calling. As the seed of Abraham, the children of Israel were chosen by God to be a separate people, holy to the Lord. God’s design was for them to be a light to the Gentiles so that they, too, might know God (Genesis 18:17–19; Isaiah 42, 49). Instead, the Israelites chased foreign gods and betrayed their calling (Ezekiel 23; Hosea 11). But God, who knew they would do this, had already promised to restore His kingdom to Israel after they rebelled and then eventually repented (Deuteronomy 30:1–10). So God sent His Son, preceded by a forerunner, to invite Israel to “repent, for the Kingdom of heaven is at hand” (Matthew 3:2; 4:17).
However, when Jesus revealed Himself as the promised Davidic King who would restore Israel (Matthew 11—12; Acts 3:19–22), He was rejected by the Jews, exactly as Isaiah had prophesied (Isaiah 52—53). Jesus therefore called His disciples to fulfill Abraham’s commission to bless the nations (Genesis 12:2–3) by preaching the gospel of the Kingdom to all nations until the end of this age (Matthew 28:18–20). Paul thus preached the gospel of the Kingdom to the Jews and was repeatedly rejected (Acts 13—28); in consequence, Paul brought the good news to the Gentiles, who in turn became Abraham’s spiritual seed by faith and heirs of the promises to Abraham and his seed (Galatians 3—4). This is what Paul meant in Romans 11 by the Gentiles being “grafted” into the “olive tree” and nourished by the “root” (the promises to Abraham). The tree thus signifies the collective people of God; the “wild branches” grafted in are Gentile believers; the “natural branches” that are cut off are the Jews in unbelief. Jewish believers remain in the tree but are joined with Gentiles and “made” into a “new body,” the Church (Ephesians 2:11–22).
Paul anticipated a question that would surely arise among his Gentile readers: “I say then, have they stumbled that they should fall?” (Romans 11:1)—Gentile believers would be tempted to dismiss Israel because it appeared they would never recover. Even today, there are those who advocate supersessionism or replacement theology, which holds that the Church has completely replaced Israel and will inherit the promises to be fulfilled only in a spiritual sense. In other words, according to this view, ethnic Israel is forever excluded from the promises—the Jews will not literally inherit the Promised Land. What then would happen to Israel? What about the Old Testament prophecies that Israel as a nation would repent and be re-gathered to the land in the last days as a permanent possession (Deuteronomy 30:1–10)?
Romans 11 thus conclusively shows Gentile believers that God is not yet “done” with Israel, who has only temporarily lost the privilege of representing God as His people. Since “the gifts and calling of God are irrevocable” (11:29), “all Israel will be saved” in order to fulfill God’s covenant with ethnic Israel (11:25–28), including the promise of land inheritance (Deuteronomy 30:1–10).
While the “natural branches” were cut off because Israel failed, God’s purposes are not complete until Israel is also grafted back into the people of God to share in the promises to Abraham and his seed. This brings full circle God’s larger redemptive plan (Romans 11:30–36) for both Jews and Gentiles as distinct populations within the people of God in the Davidic (or Millennial) Kingdom. Indeed, the prophets saw this Kingdom as the “final form” of the olive tree, so that Israel—reversing roles—would then bless the Gentiles, enabling them to join the people of God (see Zechariah 8:13, 20–23).

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed