Elijah was a mighty prophet during a turbulent time in Israel’s history. The nation had turned away from the Lord to worship Baal, and King Ahab had formed an alliance with Sidon by marrying their princess, Jezebel. Elijah was sent to show Israel the evil of their ways and encourage them to return to the Lord. Learn more about his ministry in this latest installment of our Biblical Figures series.
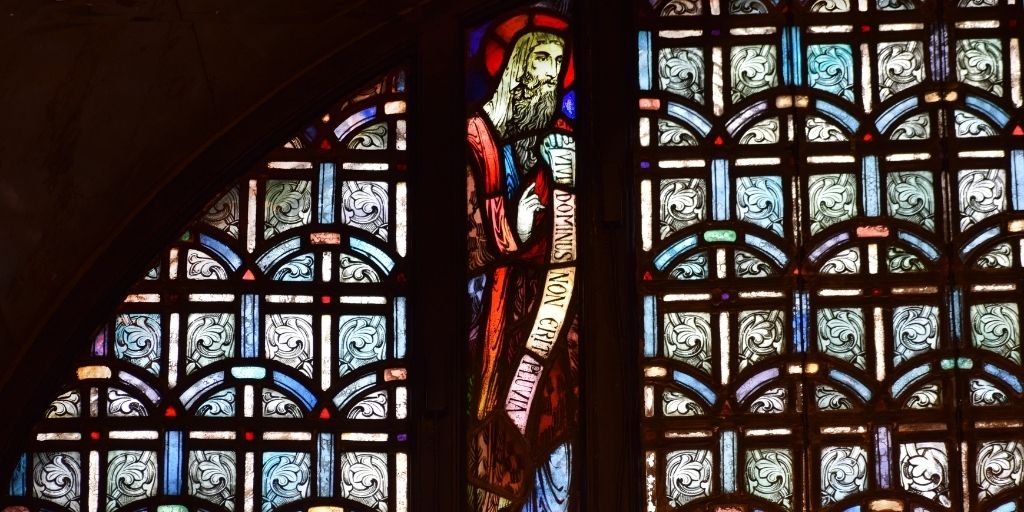
Elijah shown in stained glass in the Great Upper ChurchElijah and the WidowElijah is first mentioned in 1 Kings 17, where he proclaimed a drought as penalty for the evil deeds of the kings of Israel. During this time, ravens brought him food, and he lived by a seasonal river until it dried up. The Lord then told him to visit a widow in Zarephath for food and water. Once he arrived, her jar of flour and jug of oil did not run dry. While he was staying there, her son fell ill and died. Elijah pleaded with the Lord and stretched himself on top of the child three times, restoring him to life.
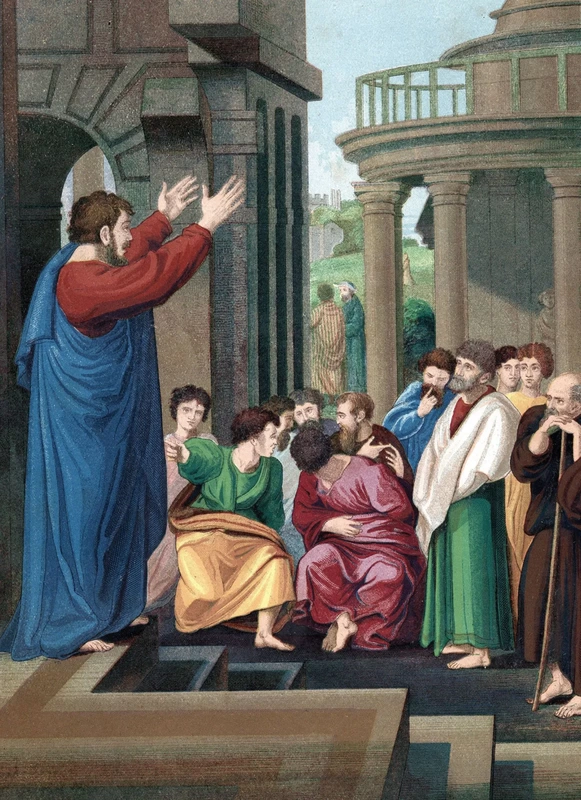
The True GodElijah then presented himself to King Ahab, telling him to summon the prophets of Baal and Asherah on Mount Carmel, along with all the people of Israel. He confronted the people and told them that if they prepared a sacrifice and called on Baal, he would prepare a sacrifice and call on the Lord. Whichever caught fire would then demonstrate who was the true God. The worshippers of Baal prepared their sacrifice and called upon him from morning until noon, with no answer.
Then Elijah rebuilt the altar of the Lord, prepared the sacrifice, and poured four jugs of water on it. He called upon the Lord, and the Lord answered him:
The Lord’s fire came down and devoured the burnt offering, wood, stones, and dust, and lapped up the water in the trench. Seeing this, all the people fell prostrate and said, “The Lord is God! The Lord is God!”
— 1 Kings 18:38-39
Elijah Fears for His Life: after this, the prophets of Baal were seized and killed. When King Ahab told his wife Jezebel what Elijah had done, she vowed to kill him. Elijah was terrified and fled into the desert, where he prayed for the Lord to take his life, then fell asleep under a broom tree. A messenger from the Lord came to him twice, urging him to eat and drink. After doing so, he journeyed 40 days in the wilderness to Mt. Horeb, where he hid in a cave. The voice of the Lord came to him and commanded him to stand out on the mountain.
A violent wind came by, followed by an earthquake, then a fire. But the Lord was not in any of them; instead, He spoke to Elijah in a quiet voice:
When he heard this, Elijah hid his face in his cloak and went out and stood at the entrance of the cave. A voice said to him, Why are you here, Elijah? He replied, “I have been most zealous for the Lord, the God of hosts, but the Israelites have forsaken your covenant. They have destroyed your altars and murdered your prophets by the sword. I alone remain, and they seek to take my life.” The Lord said to him: Go back! Take the desert road to Damascus. When you arrive, you shall anoint Hazael as king of Aram. You shall also anoint Jehu, son of Nimshi, as king of Israel, and Elisha, son of Shaphat of Abel-meholah, as prophet to succeed you. Anyone who escapes the sword of Hazael, Jehu will kill. Anyone who escapes the sword of Jehu, Elisha will kill. But I will spare seven thousand in Israel—every knee that has not bent to Baal, every mouth that has not kissed him. — 1 Kings 19:13-18
After receiving these instructions, Elijah returned to civilization and recruited Elisha to minister with him.
Elijah and AhaziahSoon after, King Ahab died and was succeeded by his son, Ahaziah. After Ahaziah suffered an injury, he sought the assistance of the god of Ekron to see whether he would recover. Elijah confronted him for rejecting the Lord, which made him angry. In his rage, Ahaziah then sent a captain with fifty men to kill Elijah:
The prophet was seated on a hilltop when he found him. He said, “Man of God, the king commands you, ‘Come down.’” Elijah answered the captain, “Well, if I am a man of God, may fire come down from heaven and consume you and your fifty men.” And fire came down from heaven and consumed him and his fifty men. — 2 Kings 1:9-10
This happened a second time; the king sent fifty men, and they were again struck down with fire. A third commander came, and he begged Elijah to spare the lives of him and his men. The Lord told Elijah not to be afraid of them, so he went down with them to the king. He told the king that because he turned away from the Lord, he would die. True to Elijah’s warning, the king was struck down by the Lord.
Elijah is Taken Up
Elijah being taken into heaven is depicted in the lower portion of the Ascension Chapel of the Great Upper ChurchWhen Elijah and Elisha traveled from Bethel to Jericho, Elijah tried to leave Elisha, but Elisha would not let him. The other prophets of the cities asked him repeatedly whether he knew that Elijah would leave him, and Elisha responded that he did. After they crossed the Jordan, Elijah asked Elisha if there was anything that he could do before he was taken up into heaven. Elisha asked to be given a double portion of his spirit, and Elijah said that was a difficult request, but that it would come to pass if he was able to see him taken up. Then a fiery chariot and horses came between them, and Elisha saw a whirlwind take Elijah to heaven.
What We Can Learn from ElijahEven in the face of adversity and discouragement, Elijah remained faithful. Throughout the Bible, he is held up as an example of godliness and might. Not only is he mentioned later in the Old Testament, but also in all four gospels and two epistles. He even appears at the transfiguration with Jesus, and when Jesus began his ministry, some thought that He was Elijah returned to earth.
The story of Elijah can be a comfort and an encouragement to us. Being a strong person of God does not mean that we will never feel discouraged, but rather, it means looking to God when faced with adversity. Elijah felt alone, and didn’t understand God’s plan, but he still searched God out. In return, he constantly saw God’s power displayed in his weakness: when He brought the widow’s son back from the dead, when He triumphed on Mt. Carmel, and when He rained down fire from heaven upon the king’s men. For his faithfulness, Elijah was one of the few individuals in the Bible to be taken into heaven.
Elijah in the BasilicaElijah is depicted in multiple areas of the Basilica, including the east buttress of the south entrance, a lunette window in the west apse of the Crypt Church, a window in the west transept of the Great Upper Church, and in the Ascension Chapel of the Upper Church.
Elijah (/ɪˈlaɪdʒə/ il-EYE-jə; Hebrew: אֵלִיָּהוּ, ʾĒlīyyāhū, meaning "My God is Yahweh[10]/YHWH";[11][12]
Greek form: Elias[a] /ɪˈlaɪəs/ il-EYE-əs) was, according to the Books of Kings in the Hebrew Bible, a prophet and a miracle worker who lived in the northern kingdom of Israel[13]during the reign of King Ahab (9th century BCE). In 1 Kings 18, Elijah defended the worship of the Hebrew God over that of the Canaanite deity Baal. God also performed many miracles through Elijah, including resurrection, bringing fire down from the sky, and entering heaven alive "by fire".[14] He is also portrayed as leading a school of prophets known as "the sons of the prophets".[15] Following his ascension, Elisha, his disciple and most devoted assistant, took over his role as leader of this school. The Book of Malachi prophesies Elijah's return "before the coming of the great and terrible day of the LORD",[16] making him a harbinger of the Messiah and of the eschaton in various faiths that revere the Hebrew Bible. References to Elijah appear in Sirach, the New Testament, the Mishnah and Talmud, the Quran, the Book of Mormon, the Doctrine and Covenants, and Baháʼí writings.
Elijah
Prophet Elijah detailed in the Madonna and Child with Saints by Andrea di Bonaiuto
- Prophet
- Father of Carmelites
Bornc. 900 BCE
possibly Tishbe
Diedc. 849 BCE[1]
near Jericho
Feast July 20
In Judaism, Elijah's name is invoked at the weekly Havdalah rite that marks the end of Shabbat, and Elijah is invoked in other Jewish customs, among them the Passover Seder and the brit milah (ritual circumcision). He appears in numerous stories and references in the Haggadah and rabbinic literature, including the Babylonian Talmud. According to the Hebrew Bible, Elijah will return during the End of Times.[17]
The Christian New Testament notes that some people thought that Jesus was, in some sense, Elijah,[18] but it also makes clear that John the Baptist is "the Elijah" who was promised to come in Malachi 3:1; 4:5.[19] According to accounts in all three of the Synoptic Gospels, Elijah appeared with Moses during the Transfiguration of Jesus.
Map of Israel as it was in the 9th century BCE.
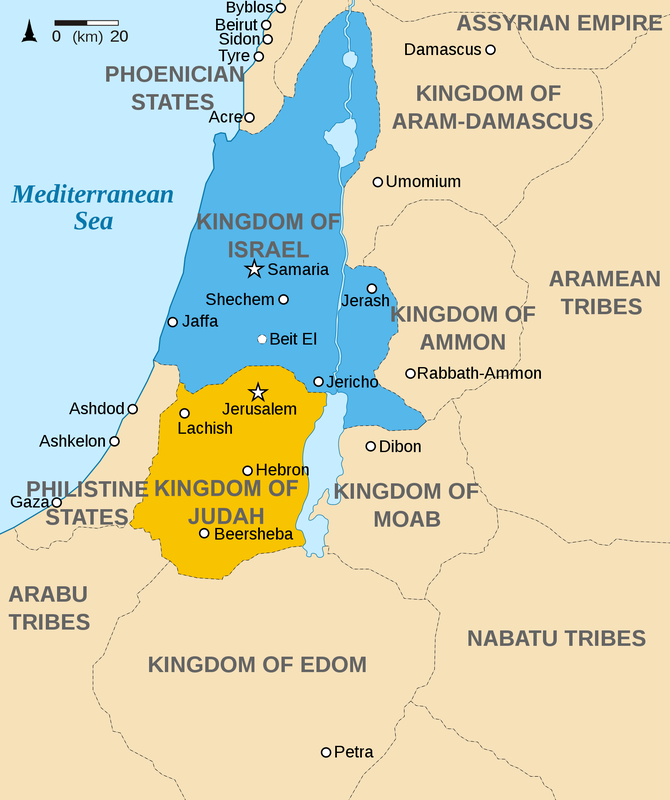
Blue is the Kingdom of Israel. Golden yellow is the Kingdom of Judah.[22]According to the Bible, by the 9th century BCE, the Kingdom of Israel, once united under Solomon, divided into the northern Kingdom of Israel and the southern Kingdom of Judah (which retained the historical capital of Jerusalem along with its Temple). Omri, King of Israel, continued policies dating from the reign of Jeroboam, contrary to religious law, that were intended to reorient religious focus away from Jerusalem: encouraging the building of local temple altars for sacrifices, appointing priests from outside the family of the Levites, and allowing or encouraging temples dedicated to Baal, an important deity in ancient Canaanite religion.[23][24] Omri achieved domestic security with a marriage alliance between his son Ahab and princess Jezebel, a worshipper of Baal and the daughter of the king of Sidon in Phoenicia.[b] These solutions brought security and economic prosperity to Israel for a time,[27] but did not bring peace with the Israelite prophets, who advocated a strict deuteronomic interpretation of the religious law.
Under Ahab's kingship tensions exacerbated. Ahab built a temple for Baal, and his wife Jezebel brought a large entourage of priests and prophets of Baal and Asherah into the country. In this context Elijah is introduced in 1 Kings 17:1 as Elijah "the Tishbite". He warns Ahab that there will be years of catastrophic drought so severe that not even dewwill form, because Ahab and his queen stand at the end of a line of kings of Israel who are said to have "done evil in the sight of the Lord".
Books of KingsEditNo background for the person of Elijah is given except for his brief characterization as a Tishbite. His name in Hebrew means "My God is Yahweh", and may be a title applied to him because of his challenge to worship of Baal.[28][29][30][31][32]
As told in the Hebrew Bible, Elijah's challenge is bold and direct. Baal was the Canaanite god responsible for rain, thunder, lightning, and dew. Elijah thus, when he initially announces the drought, not only challenges Baal on behalf of God himself, but he also challenges Jezebel, her priests, Ahab and the people of Israel.[33]
Elijah in the wilderness, by Washington Allston
Widow of Zarephath
Main article: Raising of the son of the widow of ZarephathAfter Elijah's confrontation with Ahab, God tells him to flee out of Israel, to a hiding place by the brook Chorath, east of the Jordan, where he will be fed by ravens.[34][22] When the brook dries up, God sends him to a widow living in the town of Zarephath in Phoenicia.
When Elijah finds her and asks to be fed, she says that she does not have sufficient food to keep her and her own son alive. Elijah tells her that God will not allow her supply of flour or oil to run out, saying, "Do not be afraid ... For thus says the Lord the God of Israel: The jar of meal will not be emptied and the jug of oil will not fail until the day that the Lord sends rain on the earth."[35] She feeds him the last of their food, and Elijah's promise miraculously comes true.
Elijah reviving the Son of the Widow of Zarephath by Louis HersentSome time later the widow's son dies and the widow cries, "You have come to me to bring my sin to remembrance, and to cause the death of my son!"[36] Elijah prays that God might restore her son so that the trustworthiness of God's word might be demonstrated, and "[God] listened to the voice of Elijah; the life of the child came into him again, and he revived."[37] This is the first instance of raising the dead recorded in Scripture. The widow cried, "the word of the Lord in your mouth is truth."[38]
After more than three years of drought and famine, God tells Elijah to return to Ahab and announce the end of the drought. While on his way, Elijah meets Obadiah, the head of Ahab's household, who had hidden a hundred Jewish prophets from Jezebel's violent purge. Obadiah fears that when he reports to Ahab about Elijah's whereabouts, Elijah would disappear, provoking Ahab to execute him. Elijah reassures Obadiah and sends him to Ahab.
Challenge to Baal
Elijah's offering is consumed by fire from heaven in a stained glass window at St. Matthew's German Evangelical Lutheran Church in Charleston, South Carolina.When Ahab confronts Elijah, he denounces him as being the "troubler of Israel" but Elijah retorts that Ahab himself is the one who troubled Israel by allowing the worship of false gods.
At Elijah's instruction, Ahab summons the people of Israel, 450 prophets of Baal, and 400 prophets of Asherah to Mount Carmel. Elijah then berates the people for their acquiescence in Baal worship: "How long will you go limping with two different opinions? If the LORD is God, follow him; but if Baal, then follow him."[39]
Elijah proposes a direct test of the powers of Baal and Yahweh: he and Baal's prophets will each take one of two bulls, prepare it for sacrifice and lay it on wood, but put no fire to it. The prophets of Baal choose and prepare a bull accordingly. Elijah then invites them to pray for fire to light the sacrifice. They pray from morning to noon without success. Elijah ridicules their efforts. "At noon Elijah mocked them, saying, 'Cry aloud! Surely he is a god; either he is meditating, or he has wandered away, or he is on a journey, or perhaps he is asleep and must be awakened.'"[40] They respond by shouting louder and slashing themselves with swords and spears. They continue praying until evening without success.
Elijah then repairs Yahweh's altar with twelve stones, representing the twelve tribes of Israel. Elijah digs a trench around it and prepares the other bull for sacrifice as before. He then orders that the sacrifice and altar be drenched with water from "four large jars" poured three times, filling also the trench.[41] He asks Yahweh to accept the sacrifice. Fire falls from the sky, consuming the sacrifice, the stones of the altar itself, the earth and the water in the trench as well. When the people see this, they declare, "The LORD—he is God; the LORD—he is God."[42] Elijah then orders them to seize the prophets of Baal, which they do, and Elijah kills them. Then the rains begin, signaling the end of the famine.
Mount HorebEditJezebel, enraged that Elijah had killed Baal's prophets, threatens to kill Elijah.[43] Elijah flees to Beersheba in Judah, continues alone into the wilderness, and finally sits down under a shrub, praying for death. He falls asleep under the tree; the angel of the Lord touches him and tells him to wake up and eat. When he awakens he finds bread and a jar of water. He eats, drinks, and goes back to sleep. The angel comes a second time and tells him to eat and drink because he has a long journey ahead of him.
Elijah travels for forty days and forty nights to Mount Horeb,[44] where Moses had received the Ten Commandments. Elijah is the only person described in the Bible as returning to Horeb, after Moses and his generation had left Horeb several centuries before. He seeks shelter in a cave. Elijah is told to "Go out and stand on the mountain in the presence of the LORD, for the LORD is about to pass by."[45] There is a powerful wind, an earthquake and fire, but Yahweh is not in any of them. Then a gentle whisper comes to Elijah. Yahweh sends him out again, this time to Damascus to anoint Hazael as king of Aram, Jehu as king of Israel, and Elisha as his replacement.
Widow of Zarephath
Main article: Raising of the son of the widow of Zarephath
After Elijah's confrontation with Ahab, God tells him to flee out of Israel, to a hiding place by the brook Chorath, east of the Jordan, where he will be fed by ravens.[34][22] When the brook dries up, God sends him to a widow living in the town of Zarephath in Phoenicia.
When Elijah finds her and asks to be fed, she says that she does not have sufficient food to keep her and her own son alive. Elijah tells her that God will not allow her supply of flour or oil to run out, saying, "Do not be afraid ... For thus says the Lord the God of Israel: The jar of meal will not be emptied and the jug of oil will not fail until the day that the Lord sends rain on the earth."[35] She feeds him the last of their food, and Elijah's promise miraculously comes true.
Elijah reviving the Son of the Widow of Zarephath by Louis HersentSome time later the widow's son dies and the widow cries, "You have come to me to bring my sin to remembrance, and to cause the death of my son!"[36] Elijah prays that God might restore her son so that the trustworthiness of God's word might be demonstrated, and "[God] listened to the voice of Elijah; the life of the child came into him again, and he revived."[37] This is the first instance of raising the dead recorded in Scripture. The widow cried, "the word of the Lord in your mouth is truth."[38]
After more than three years of drought and famine, God tells Elijah to return to Ahab and announce the end of the drought. While on his way, Elijah meets Obadiah, the head of Ahab's household, who had hidden a hundred Jewish prophets from Jezebel's violent purge. Obadiah fears that when he reports to Ahab about Elijah's whereabouts, Elijah would disappear, provoking Ahab to execute him. Elijah reassures Obadiah and sends him to Ahab.
Challenge to Baal
Elijah's offering is consumed by fire from heaven in a stained glass window at St. Matthew's German Evangelical Lutheran Church in Charleston, South Carolina.When Ahab confronts Elijah, he denounces him as being the "troubler of Israel" but Elijah retorts that Ahab himself is the one who troubled Israel by allowing the worship of false gods.
At Elijah's instruction, Ahab summons the people of Israel, 450 prophets of Baal, and 400 prophets of Asherah to Mount Carmel. Elijah then berates the people for their acquiescence in Baal worship: "How long will you go limping with two different opinions? If the LORD is God, follow him; but if Baal, then follow him."[39]
Elijah proposes a direct test of the powers of Baal and Yahweh: he and Baal's prophets will each take one of two bulls, prepare it for sacrifice and lay it on wood, but put no fire to it. The prophets of Baal choose and prepare a bull accordingly. Elijah then invites them to pray for fire to light the sacrifice. They pray from morning to noon without success. Elijah ridicules their efforts. "At noon Elijah mocked them, saying, 'Cry aloud! Surely he is a god; either he is meditating, or he has wandered away, or he is on a journey, or perhaps he is asleep and must be awakened.'"[40] They respond by shouting louder and slashing themselves with swords and spears. They continue praying until evening without success.
Elijah then repairs Yahweh's altar with twelve stones, representing the twelve tribes of Israel. Elijah digs a trench around it and prepares the other bull for sacrifice as before. He then orders that the sacrifice and altar be drenched with water from "four large jars" poured three times, filling also the trench.[41] He asks Yahweh to accept the sacrifice. Fire falls from the sky, consuming the sacrifice, the stones of the altar itself, the earth and the water in the trench as well. When the people see this, they declare, "The LORD—he is God; the LORD—he is God."[42] Elijah then orders them to seize the prophets of Baal, which they do, and Elijah kills them. Then the rains begin, signaling the end of the famine.
Mount HorebEditJezebel, enraged that Elijah had killed Baal's prophets, threatens to kill Elijah.[43] Elijah flees to Beersheba in Judah, continues alone into the wilderness, and finally sits down under a shrub, praying for death. He falls asleep under the tree; the angel of the Lord touches him and tells him to wake up and eat. When he awakens he finds bread and a jar of water. He eats, drinks, and goes back to sleep. The angel comes a second time and tells him to eat and drink because he has a long journey ahead of him.
Elijah travels for forty days and forty nights to Mount Horeb,[44] where Moses had received the Ten Commandments. Elijah is the only person described in the Bible as returning to Horeb, after Moses and his generation had left Horeb several centuries before. He seeks shelter in a cave. Elijah is told to "Go out and stand on the mountain in the presence of the LORD, for the LORD is about to pass by."[45] There is a powerful wind, an earthquake and fire, but Yahweh is not in any of them. Then a gentle whisper comes to Elijah. Yahweh sends him out again, this time to Damascus to anoint Hazael as king of Aram, Jehu as king of Israel, and Elisha as his replacement.
Vineyard of Naboth
Elijah encounters Ahab again in 1 Kings 21, after Ahab has acquired possession of a vineyard by murder. Ahab desires to have the vineyard of Naboth of Jezreel. He offers a better vineyard or a fair price for the land. But Naboth tells Ahab that God has told him not to part with the land. Ahab accepts this answer with sullen bad grace. Jezebel, however, plots a method for acquiring the land. She sends letters, in Ahab's name, to the elders and nobles who lived near Naboth. They are to arrange a feast and invite Naboth. At the feast, false charges of cursing God and Ahab are to be made against him. The plot is carried out and Naboth is stoned to death. When word comes that Naboth is dead, Jezebel tells Ahab to take possession of the vineyard.
God again speaks to Elijah and sends him to confront Ahab with a question and a prophecy: "Have you killed, and also taken possession?" and, "In the place where dogs licked up the blood of Naboth, dogs will also lick up your blood."[46] Ahab begins the confrontation by calling Elijah his enemy. Elijah responds by throwing the charge back at him, telling him that he has made himself the enemy of God by his own actions. Elijah tells Ahab that his entire kingdom will reject his authority; that Jezebel will be eaten by dogs within Jezreel; and that his family will be consumed by dogs as well (if they die in a city) or by birds (if they die in the country). When Ahab hears this he repents to such a degree that God relents in punishing Ahab but will punish Jezebel and their son: Ahaziah.
Ahaziah
Elijah destroying the messengers of Ahaziah (illustration by Gustave Doré from the 1866 La Sainte Bible)Elijah's story continues now from Ahab to an encounter with Ahaziah (2 Kings 1). The scene opens with Ahaziah seriously injured in a fall. He sends to the priests of Baalzebub in Ekron, outside the kingdom of Israel, to know if he will recover. Elijah intercepts his messengers and sends them back to Ahaziah with a message "Is it because there is no God in Israel that you are sending to inquire of Baal-zebub, the god of Ekron?"[44][47] Ahaziah asks the messengers to describe the person who gave them this message. They tell him he was a hairy man with a leather belt around his waist and he instantly recognizes the description as Elijah the Tishbite.
Ahaziah sends out three groups of soldiers to arrest Elijah. The first two are destroyed by fire which Elijah calls down from heaven. The leader of the third group asks for mercy for himself and his men. Elijah agrees to accompany this third group to Ahaziah, where he gives his prophecy in person. Ahaziah dies without recovering from his injuries in accordance with Elijah's word.[48]
Departure
Elijah's chariot in the whirlwind. Fresco, Anagni Cathedral, c. 1250According to 2 Kings 2:3–9, Elisha (Eliseus) and "the sons of the prophets" knew beforehand that Elijah would one day be assumed into heaven. Elisha asked Elijah to "let a double portion" of Elijah's "spirit" be upon him. Elijah agreed, with the condition that Elisha would see him be "taken".
Elijah, in company with Elisha, approaches the Jordan. He rolls up his mantle and strikes the water.[49]The water immediately divides and Elijah and Elisha cross on dry land. Suddenly, a chariot of fire and horses of fire appear[44] and Elijah is lifted up in a whirlwind. As Elijah is lifted up, his mantle falls to the ground and Elisha picks it up.
Books of Chronicles: Books of Chronicles
Elijah is mentioned once more in 2 Chronicles 21:12, which will be his final mention in the Hebrew Bible. A letter is sent under the prophet's name to Jehoram of Judah. It tells him that he has led the people of Judah astray in the same way that Israel was led astray. The prophet ends the letter with a prediction of a painful death.
This letter is a puzzle to readers for several reasons. First, it concerns a king of the southern kingdom, while Elijah concerned himself with the kingdom of Israel. Second, the message begins with "Thus says YHVH, God of your father David..." rather than the more usual "...in the name of YHVH the God of Israel." Also, this letter seems to come after Elijah's ascension into the whirlwind.[citation needed]
Michael Wilcock, formerly of Trinity College, Bristol, suggests a number of possible reasons for this letter, among them that it may be an example of a better known prophet's name being substituted for that of a lesser known prophet.[50] John Van Seters, however, rejects the letter as having any connection with the Elijah tradition.[51] However, Wilcock argues that Elijah's letter "does address a very 'northern' situation in the southern kingdom", and thus is authentic.[52]
In MalachiEditWhile the final mention of Elijah in the Hebrew Bible is in the Book of Chronicles, the Christian Bible’s reordering places the Book of Malachi (which prophecies a messiah) as the final book of the Old Testament, before the New Testament gospels.[53] Thus, Elijah's final Old Testament appearance is in the Book of Malachi, where it is written, "Behold, I will send you Elijah the prophet before the great and awesome day of the Lord comes. And he will turn the hearts of fathers to their children and the hearts of children to their fathers, lest I come and strike the land with a decree of utter destruction."[54]
Historicity
Scholars generally agree that a prophet named Elijah existed in the Kingdom of Israel during the reigns of Kings Ahab and Ahaziah.[55] In the opinion of some, however, the biblical presentation of the prophet cannot be taken as historical documentation of his activity. The biblical texts present his career through the eyes of popular legend and subsequent theological reflection, which consider him a personality of heroic proportions. In this process his actions and relations to the people and the King became stereotyped, and the presentation of his behavior paradigmatic.[56]
In the Aggadah, Talmud, and extra-canonical books
Jewish legends about Elijah abound in the aggadah, which is found throughout various collections of rabbinic literature, including the Babylonian Talmud. This varied literature does not merely discuss his life, but has created a new history of him, which, beginning with his death—or "translation"—ends only with the close of the history of the human race. The volume of references to Elijah in Jewish Tradition stands in marked contrast to that in the Canon. As in the case of most figures of Jewish legend, so in the case of Elijah, the biblical account became the basis of later legend. Elijah the precursor of the Messiah, Elijah zealous in the cause of God, Elijah the helper in distress: these are the three leading notes struck by the Aggadah, endeavoring to complete the biblical picture with the Elijah legends. His career is extensive, colorful, and varied. He has appeared the world over in the guise of a beggar and scholar.
From the time of Malachi, who says of Elijah that God will send him before "the great and dreadful day",[57] down to the later stories of the Chasidic rabbis, reverence and love, expectation and hope, were always connected in the Jewish consciousness with Elijah.
OriginEditThree different theories regarding Elijah's origin are presented in the Aggadah literature: (1) he belonged to the tribe of Gad,[58] (2) he was a Benjamite from Jerusalem, identical with the Elijah mentioned in 1 Chronicles 8:27, and (3) he was a priest.
Many Christian Church fathers also[59] have stated that Elijah was a priest. Some rabbis have speculated that he should be identified with Phinehas.[60]
According to later Kabbalistic literature, Elijah was really an angel in human form,[44] so that he had neither parents nor offspring.[61]
The Midrash Rabbah Exodus 4:2 states "Elijah should have revived his parents as he had revived the son of the Zarephathite" indicating he surely had parents.
The Talmud states "Said he [Rabbah] to him (Elijah): Art thou not a priest: why then dost thou stand in a cemetery?"[62]
Zeal for God
The statue of Elijah at the Saint Elias Cathedral, Aleppo, SyriaA midrash[which?] tells that they even abolished the sign of the covenant, and the prophet had to appear as Israel's accuser before God.[63][clarification needed]
In the same cave where God once appeared to Moses and revealed Himself as gracious and merciful, Elijah was summoned to appear before God. By this summons he perceived that he should have appealed to God's mercy, instead of becoming Israel's accuser. The prophet, however, remained relentless in his zeal and severity, so that God commanded him to appoint his successor.[64]
The vision in which God revealed Himself to Elijah gave him at the same time a picture of the destinies of man, who has to pass through "four worlds." This world was shown to the prophet by God through symbolism: in the form of the wind, since the world disappears as the wind; storm is the day of death, before which man trembles; fire is the judgment in Gehenna; and the stillness is the last day.[65]
Three years after this vision, Elijah was "translated."[66] Concerning the place to which Elijah was transferred, opinions differ among Jews and Christians, but the old view was that Elijah was received among the heavenly inhabitants, where he records the deeds of men.[67]
But as early as the middle of the 2nd century, when the notion of translation to heaven underwent divergent possible interpretations by Christian theologians, the assertion was made that Elijah never entered into heaven proper.[68] In later literature paradise is generally designated as the abode of Elijah,[69] but since the location of paradise is itself uncertain, the last two statements may be identical.
EcclesiasticusEditAt the appointed time, it is written, you are destined to calm the wrath of God before it breaks out in fury, to turn the hearts of parents to their children, and to restore the tribes of Jacob.
— A line in the Wisdom of Jesus ben Sira describing Elijah's mission (Ecclesiasticus 48:10).In the Wisdom of Jesus ben Sira,[70] his tasks are altered to:
- herald the eschaton,
- calm God's fury,
- restore familial peace, and
- restore the 12 tribes.
In Judaism
Elijah's chair
"Chair of Elijah" used during the brit milah (circumcision) ceremony. The Hebrewinscription reads "This is the chair of Elijah, remembered for Good."At Jewish circumcision ceremonies, a chair is set aside for the use of the prophet Elijah. Elijah is said to be a witness at all circumcisions when the sign of the covenant is placed upon the body of the child. This custom stems from the incident at Mount Horeb:[71] Elijah had arrived at Mount Horeb after the demonstration of God's presence and power on Mount Carmel.[72] God asks Elijah to explain his arrival, and Elijah replies: "I have been very jealous for the Lord, the God of hosts; for the people of Israel have forsaken thy covenant, thrown down thy altars, and slain thy prophets with the sword; and I, even I only, am left; and they seek my life, to take it away".[73] According to Rabbinic tradition, Elijah's words were patently untrue,[74] and since Elijah accused Israel of failing to uphold the covenant, God would require Elijah to be present at every covenant of circumcision.[75][76]
Elijah's cupEditSee also: Passover SederIn the Talmudic literature, Elijah would visit rabbis to help solve particularly difficult legal problems. Malachi had cited Elijah as the harbinger of the eschaton. Thus, when confronted with reconciling impossibly conflicting laws or rituals, the rabbis would set aside any decision "until Elijah comes".[77]
One such decision was whether the Passover Seder required four or five cups of wine. Each serving of wine corresponds to one of the "four expressions of redemption" in the Book of Exodus:
I am the Lord, and I will bring you out from under the burdens of the Egyptians, and I will deliver you from their bondage, and I will redeem you with an out-stretched arm and with great acts of judgment, and I will take you for my people, and I will be your God; and you shall know that I am the Lord your God, who has brought you out from under the burdens of the Egyptians."[78]
The next verse, "And I will bring you into the land which I swore to give to Abraham, to Isaac, and to Jacob; I will give it to you for a possession. I am the Lord."[79] was not fulfilled until the generation following the Passover story, and the rabbis could not decide whether this verse counted as part of the Passover celebration (thus deserving of another serving of wine). Thus, a cup was left for the arrival of Elijah.
In practice the fifth cup has come to be seen as a celebration of future redemption. Today, a place is reserved at the seder table and a cup of wine is placed there for Elijah. During the seder, the door of the house is opened and Elijah is invited in. Traditionally, the cup is viewed as Elijah's and is used for no other purpose.[80][81]
HavdalahEditSee also: HavdalahHavdalah is the ceremony that concludes the Sabbath Day (Saturday evening in Jewish tradition). As part of the concluding hymn, an appeal is made to God that Elijah will come during the following week. "Elijah the Prophet, Elijah the Tishbite, Elijah from Gilead. Let him come quickly, in our day with the messiah, the son of David."[80]
New Testament
A Northern Russian icon from ca. 1290 showing the ascent of Elijah toward heaven
In the New Testament, Jesus would say for those who believed, John the Baptist was Elijah, who would come before the "great and terrible day" as predicted by Malachi.
Some English translations of the New Testament use Elias, a Greek form of the name. In the King James Version, "Elias" appears only in the texts translated from Greek.
John the BaptistEditJohn the Baptist preached a message of repentance and baptism. He predicted the day of judgment using imagery similar to that of Malachi. He also preached that the Messiah was coming. All of this was done in a style that immediately recalled the image of Elijah to his audience. He wore a coat of camel's hair secured with a leather girdle.[94] He also frequently preached in wilderness areas near the Jordan River.
In the Gospel of John, when John the Baptist was asked by a delegation of priests (present tense) "Art thou Elias", he replied "I am not".[95] Matthew 11:14 and Matthew 17:10–13 however, make it clear that John was the spiritual successor to Elijah. In the Nativity of St. John the Baptist in Luke, Gabriel appears to Zechariah, John's father, and told him that John "will turn many of the sons of Israel to the Lord their God," and that he will go forth "in the spirit and power of Elijah."[96]
Elijah appeared at the Transfiguration of Jesus.
TransfigurationEditElijah makes an appearance in the New Testament during an incident known as the Transfiguration.[97]
At the summit of an unnamed mount, Jesus' face begins to shine. The disciples who are with Him hear the voice of God announce that Jesus is "My beloved Son." The disciples also see Moses and Elijah appear and talk with Jesus. This apparently relates to how both Elijah and Moses, the latter according to tradition but not the Bible, both were translated to heaven instead of dying. Peter is so struck by the experience that he asks Jesus if they should build three "tabernacles": one for Elijah, one for Jesus and one for Moses.
There is agreement among some Christian theologians that Elijah appears to hand over the responsibility of the prophets to Jesus as the woman by the well said to Jesus "I perceive thou art a prophet."[98] Moses also likewise came to hand over the responsibility of the law for the divinely announced Son of God.[99][100]
Other references: Elijah is mentioned four more times in the New Testament: in Luke, Romans, Hebrews, and James. In Luke 4:24–27, Jesus uses Elijah as an example of rejected prophets. Jesus says, "No prophet is accepted in his own country," and then mentions Elijah, saying that there were many widows in Israel, but Elijah was sent to one in Phoenicia. In Romans 11:1–6, Paul cites Elijah as an example of God's never forsaking his people (the Israelites). Hebrews 11:35 ("Women received their dead raised to life again...") refers to both Elijah raising the son of the widow of Zarephath and Elisha raising the son of the woman of Shunem, citing both Elijah and Elisha as Old Testament examples of faith.[101][102][103] In James 5:16–18, James says, "The effectual fervent prayer of a righteous man availeth much," and then cites Elijah's prayers which started and ended the famine in Israel as examples.
In Jewish folklore: the volume of references to Elijah in folklore stands in marked contrast to that in the canon. Elijah's miraculous transferral to heaven led to speculation as to his true identity. Louis Ginzberg equates him with Phinehas the grandson of Aaron.[82][83] Because of Phinehas' zealousness for God, he and his descendants were promised, "a covenant of lasting priesthood."[84] Therefore, Elijah is a priest as well as a prophet. Elijah is also equated with the Archangel Sandalphon,[85] whose four wing beats will carry him to any part of the earth. When forced to choose between death and dishonor, Rabbi Kahana chose to leap to his death. Before he could strike the ground, Elijah/Sandalphon had appeared to catch him.[86] Yet another name for Elijah is "Angel of the Covenant"[87]



 RSS Feed
RSS Feed