Gospel,
aka,
The WORD of GOD
Parable of the Growing
Seed
The term word is used in different ways in the Bible.
In the New Testament,
there are two Greek words translated "word": rhema and logos. They have slightly different meanings. Rhema usually means “a spoken word.” For example, in Luke 1:38,
when the angel told Mary that she would be the
mother of God’s Son,
Mary replied,
"Behold,
I am the servant of the Lord;
let it be to me
according to your word
[rhema].”
Logos, however,
has a broader, more philosophical meaning. This is the term
used in John 1. It usually
implies a total message,
and is used mostly in reference to
God’s message to mankind.
For example, Luke 4:32 says that, when Jesus taught the people,
"they were amazed at his teaching,
because his
words [logos] had authority."
The people were amazed not merely by the particular
'words" Jesus chose
but by His "total message."
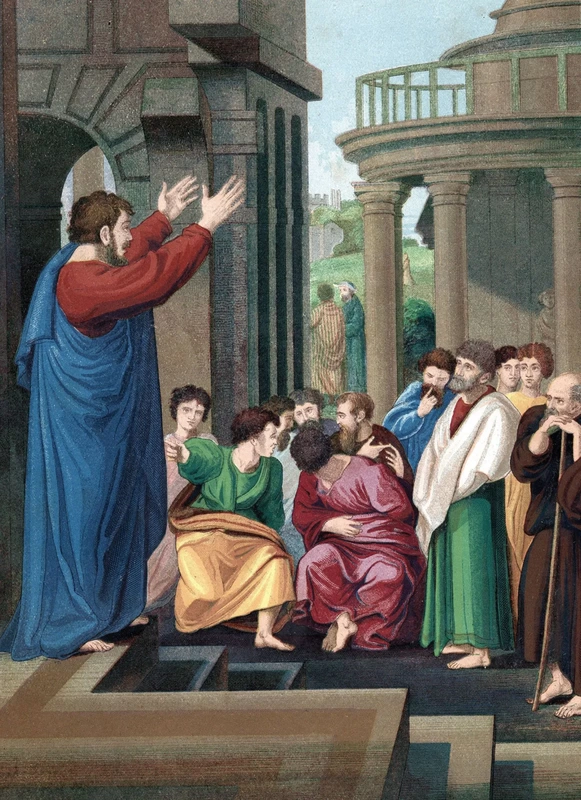
"The Word" (Logos) in John 1 is referring to Jesus. Jesus is the total Message—everything that God wants to communicate to man. The first chapter of John gives us a glimpse inside the Father/Son relationship before Jesus came to earth in human form. He preexisted with the Father (verse 1), He was involved in the creation of everything (verse 3), and He is the "light of all mankind" (verse 4). The Word (Jesus) is the full embodiment of all that is God (Colossians 1:19; 2:9; John 14:9). But God the Father is Spirit. He is invisible to the human eye. The message of love and redemption that God spoke through the prophets had gone unheeded for centuries (Ezekiel 22:26; Matthew 23:37). People found it easy to disregard the message of an invisible God and continued in their sin and rebellion. So the Message became flesh, took on human form, and came to dwell among us (Matthew 1:23; Romans 8:3; Philippians 2:5–11).
The Greeks used the word logos to refer to one’s “mind,” “reason,” or “wisdom.” John used this Greek concept to communicate the fact that Jesus, the Second Person of the Trinity, is the self-expression of God to the world. In the Old Testament, the word of God brought the universe into existence (Psalm 33:6) and saved the needy (Psalm 107:20). In chapter 1 of his Gospel, John is appealing to both Jew and Gentile to receive the eternal Christ.
Jesus told a parable in Luke 20:9–16 to explain why the Word had to become flesh. “A man planted a vineyard, rented it to some farmers and went away for a long time. At harvest time he sent a servant to the tenants so they would give him some of the fruit of the vineyard. But the tenants beat him and sent him away empty-handed. He sent another servant, but that one also they beat and treated shamefully and sent away empty-handed. He sent still a third, and they wounded him and threw him out.
“Then the owner of the vineyard said, ‘What shall I do? I will send my son, whom I love; perhaps they will respect him.’ But when the tenants saw him, they talked the matter over. ‘This is the heir,’ they said. ‘Let’s kill him, and the inheritance will be ours.’ So they threw him out of the vineyard and killed him. What then will the owner of the vineyard do to them? He will come and kill those tenants and give the vineyard to others.”
In this parable, Jesus was reminding the Jewish leaders that they had rejected the prophets and were now rejecting the Son. The Logos, the Word of God, was now going to be offered to everyone, not just the Jews (John 10:16; Galatians 2:28; Colossians 3:11). Because the Word became flesh, we have a high priest who is able to empathize with our weaknesses, one who has been tempted in every way, just as we are—yet He did not sin (Hebrews 4:15).
The way God uses His Word in the heart of an individual is mysterious and completely independent of human effort. May we be faithful in “sowing the seed,” praying for a harvest, and leaving the results to the Lord!
Jesus alerts us to “watch out for false prophets” in Matthew 7:15. He compares these false prophets to wolves in sheep’s clothing.
Jesus also tells us how to identify these false prophets: we will recognize them by their fruit (Matthew 7:20).
Throughout the Bible, people are warned about false prophets (Ezekiel 13, Matthew 24:23–27, 2 Peter 3:3). False prophets claim to speak for God, but they speak falsehood. To gain a hearing, they come to people “in sheep’s clothing, but inwardly they are ferocious wolves” (Matthew 7:15). No matter how innocent and harmless these teachers appear on the outside, they have the nature of wolves—they are intent on destroying faith, causing spiritual carnage in the church, and enriching themselves. They “secretly introduce destructive heresies,” “bring the way of truth into disrepute,” and “exploit you with fabricated stories” (2 Peter 2:1–3).
The false teachers don “sheep’s clothing” so they can mingle with the sheep without arousing suspicion. They usually are not up front about what they believe; rather, they mix in some truth with their falsehood and carefully choose their words to sound orthodox. In reality, they “follow their own ungodly desires” (Jude 1:17–18), and “they never stop sinning; they seduce the unstable; they are experts in greed” (2 Peter 3:14).
By contrast, a true prophet teaches God’s Word fully (Deuteronomy 18:20). Wolves in sheep’s clothing twist God’s Word to deceive or influence the audience for their own purposes. Satan himself masquerades as an angel of light (2 Corinthians 11:14), and his ministers masquerade as servants of righteousness (2 Corinthians 11:15).
The best way to guard against wolves in sheep’s clothing is to heed the warnings of Scripture and know the truth. A believer who “correctly handles the word of truth” (2 Timothy 2:15) and carefully studies the Bible will be able to identify false prophets. Christians must judge all teaching against what Scripture says. Believers will also be able to identify false prophets by their fruit—their words, actions, and lifestyles. Jesus said, “A tree is recognized by its fruit” (Matthew 12:33; cf. Matthew 7:20). Peter described false teachers as having “depraved conduct” and who “carouse” as “slaves of depravity” (2 Peter 2:2, 13, 19). If a teacher in the church does not live according to God’s Word, he is one of those wolves in sheep’s clothing.
Here are three specific questions to identify false prophets, or wolves in sheep’s clothing:
1) What does the teacher say about Jesus? In John 10:30, Jesus says, “I and the Father are one.” The Jews understood Jesus’ statement as a claim to be God and wanted to stone him (John 10:33). Anyone who denies Jesus as Lord (1 John 4:1–3) is a false prophet.
2) Does the teacher preach the biblical gospel? Anyone who teaches an incomplete or unbiblical gospel is to be eternally condemned (Galatians 1:9). Any gospel apart from what the Bible tells us (1 Corinthians 15:1–4) is not the true good news.
3) Does this teacher exhibit godly character qualities? Jesus said to beware of teachers whose moral behavior does not match what the Bible says. He says we will know wolves in sheep’s clothing by their fruits (Matthew 7:15–20)
It doesn’t matter how large a church a preacher has, how many books he has sold, or how many people applaud him. If he “teaches a different doctrine and does not agree with the sound words of our Lord Jesus Christ and the teaching that accords with godliness,” then he is a wolf in sheep’s clothing (1 Timothy 6:3).
The Parable of the Sheep and Goats is part of the Olivet Discourse. It is found in Matthew 25:31-46. A parable is a short, simple story of comparison. Jesus used parables to teach spiritual truths by means of earthly situations.
Jesus begins the parable by saying it concerns His return in glory to set up His kingdom (Matthew 25:31). Therefore, the setting of this event is at the beginning of the millennium, after the tribulation. All those on earth at that time will be brought before the Lord, and He will separate them “as a shepherd separates the sheep from the goats. He will put the sheep on his right and the goats on his left” (verses 32–33). The sheep are those who were saved during the tribulation; the goats are the unsaved who survived the tribulation.
The sheep on Jesus’ right hand are blessed by God the Father and given an inheritance. The reason is stated: “For I was hungry and you gave me something to eat, I was thirsty and you gave me something to drink, I was a stranger and you invited me in, I needed clothes and you clothed me, I was sick and you looked after me, I was in prison and you came to visit me” (verses 35-36). The righteous will not understand: when did they see Jesus in such a pitiful condition and help Him? “The King will reply, ‘I tell you the truth, whatever you did for one of the least of these brothers of mine, you did for me’” (verses 39-40).
The goats on Jesus’ left hand are cursed with eternal hell-fire, “prepared for the devil and his angels” (verse 41). The reason is given: they had opportunity to minister to the Lord, but they did nothing (verses 42-43). The damned ask, “Lord, when did we see you hungry or thirsty or a stranger or needing clothes or sick or in prison, and did not help you?” (verse 44). Jesus replies, “I tell you the truth, whatever you did not do for one of the least of these, you did not do for me” (verse 45).
Jesus then ends the discourse with a contrast: “They will go away to eternal punishment, but the righteous to eternal life” (verse 46).
In the Parable of the Sheep and the Goats, we are looking at man redeemed and saved, and man condemned and lost. A casual reading seems to suggest that salvation is the result of good works. The “sheep” acted charitably, giving food, drink, and clothing to the needy. The “goats” showed no charity. This seems to result in salvation for the sheep and damnation for the goats.
However, Scripture does not contradict itself, and the Bible clearly and repeatedly teaches that salvation is by faith through the grace of God and not by our good works (see John 1:12; Acts 15:11; Romans 3:22-24; Romans 4:4-8; Romans 7:24-25; Romans 8:12; Galatians 3:6-9; and Ephesians 2:8-10). In fact, Jesus Himself makes it clear in the parable that the salvation of the “sheep” is not based on their works—their inheritance was theirs “since the creation of the world” (Matthew 25:34), long before they could ever do any good works!
The good works mentioned in the parable are not the cause of salvation but the effect of salvation. As Christians we become like Christ (see Romans 8:29; 2 Corinthians 3:18; and Colossians 2:6-7). Galatians 5:22 tells us that the fruit of the Spirit is love, joy, peace, patience, kindness, goodness, gentleness, faithfulness, and self-control. Good works in a Christian’s life are the direct overflow of these traits, and are only acceptable to God because of the relationship that exists between servant and Master, the saved and their Savior, the sheep and their Shepherd (see Ephesians 2:10).
The core message of the Parable of the Sheep and Goats is that God’s people will love others. Good works will result from our relationship to the Shepherd. Followers of Christ will treat others with kindness, serving them as if they were serving Christ Himself. The unregenerate live in the opposite manner.
While “goats” can indeed perform acts of kindness and charity, their hearts are not right with God, and their actions are not for the right purpose – to honor and worship God.
The statement “you will know them by their fruit” (Matthew 7:16) is part of Jesus’ teaching about recognizing true followers and avoiding false prophets. Beginning with verse 15, we read this context: “Beware of the false prophets, who come to you in sheep’s clothing, but inwardly are ravenous wolves. You will know them by their fruits. Grapes are not gathered from thorn bushes nor figs from thistles, are they? So every good tree bears good fruit, but the bad tree bears bad fruit. A good tree cannot produce bad fruit, nor can a bad tree produce good fruit. Every tree that does not bear good fruit is cut down and thrown into the fire. So then, you will know them by their fruits” (Matthew 7:15–20).
The seventh chapter of the Gospel of Matthew is a gold mine of teaching from the popular verse 1 to the well-known parable about the wise man building his house upon the rock (verses 24–27). In verses 21–23, Jesus makes a chilling announcement to many who assumed they belonged to Him. He warned them that on Judgment Day they will hear Him say, “Depart from me. I never knew you.” Just before that warning, Jesus had indicted those who pretended to follow Him but whose lives indicated something else. He told His followers that the “fruit” of their lives proved what was inside their hearts (cf. Mark 7:20–23).
When Jesus says, “You will know them by their fruit,” what does “fruit” mean? Jesus gave the illustration of grape vines and fig trees. When we see grape vines, we expect them to contain grapes in season. We also expect fig trees to produce figs. A produce farmer who notices one of his fruit trees not bearing any fruit will cut it down. It is useless. Likewise, we would not come to a field of thistles and expect to harvest fruit. Thistles and thorn bushes can never produce fruit because of their nature. It is impossible. They have no capacity to produce anything but thorns (Matthew 12:33).
In our lives, every word and every action is fruit from our hearts. Sinners sin because that’s what is in their hearts. Thieves steal, rapists attack, and adulterers cheat because those sins are the fruit being produced from an evil heart. Bad hearts produce bad fruit. When Jesus said, “You will know them by their fruit” concerning false teachers, He was giving us a guide for identifying them. False prophets, speakers of lies, will have actions that correspond to their errant message. Just as their message is anti-God, so will be their works. They will stray from the path of righteousness.
When we repent of our sin and receive Jesus as Lord of our lives (John 1:12; Acts 2:38), He changes our hearts (2 Corinthians 5:17). Now the fruit that is produced is good fruit. Galatians 5:22 lists some of the fruit produced by a heart in tune with God. Our attitudes, actions, words, and perspectives change as we walk in fellowship with the Holy Spirit (1 John 1:6–7). When our hearts change, our fruit changes.
Many false prophets have come and gone, and many of them lived in blatant sin while preaching their message. Jim Jones openly engaged in adultery, drug use, and profanity. David Koresh had child “wives” as young as 11. False teachers might display the “fruit” of sexual immorality, greed, materialism, gluttony, and other sins while justifying their behavior and lifting themselves up as something holy. Unfortunately, many people through the years have been duped into following such characters and joining them in justifying the sin. If only they had heeded Jesus’ warning that “you will know them by their fruit.” No matter how good or convincing someone sounds, if he is bearing bad fruit, his message should be avoided.
Godly teachers will display good “fruit” such as making disciples (Matthew 28:19), using their gifts to benefit others (Romans 12:4–8), leading lost people to Jesus (James 5:20), loving their fellow believers (1 John 3:14), and seeking humble ways to do good everywhere (Jeremiah 29:7). All of these things are indications of a good heart.
Often, people profess faith in Jesus as Savior, but it is a mere profession with no real faith. Some religious groups encourage baptism, confirmation, or other religious rites that are supposed to ensure one’s future in heaven. But as time goes on, the fruit being produced in such a life looks nothing like what is clearly prescribed in the Bible (1 Peter 1:16). Some attend church services but spend the rest of their time living entirely for themselves. Some may rise to prominence, even teaching or preaching, writing books, or dominating the media, but the fruit of their lives belies their words (Matthew 24:24). Greed, deception, immorality, pride, or dishonesty defines them, making them false prophets by Jesus’ standards (2 Peter 2:1–3).
While we can never know anyone else’s heart, we can make wise assessments about other people by observing the regular fruit of their lives. All of us stumble from time to time, and we may go through seasons of bearing little fruit (1 John 1:8). But 1 John 3:4–10makes it clear that those who know God will not continue a lifestyle of bearing bad fruit. We have been transformed, and the fruit of our lives is evidence of that transformation. Apple trees don’t produce bananas, and strawberry plants don’t produce figs. This fact of nature is also true in the spiritual realm. We can identify those whose hearts have been redeemed by the fruit we see in their lives.
Throughout the Bible, the harvest carries spiritual significance. It is used in parables (Luke 8:4–8) and as a metaphor for spiritual growth and health (2 Corinthians 9:10; James 3:18). The harvest has always been a beautiful and important part of life on earth, the time when the year’s work bears fruit and the people are fed. It is symbolic of bounty, health and abundance. Israel celebrated the time of the harvest with a feast, appropriately called the Feast of Harvest (Exodus 23:16).
Jesus spoke of a spiritual harvest waiting to be reaped. As Jesus traveled, “he saw the crowds, [and] he had compassion for them, because they were harassed and helpless, like sheep without a shepherd. Then he said to his disciples, ‘The harvest is plentiful, but the laborers are few; therefore pray earnestly to the Lord of the harvest to send out laborers into his harvest’” (Matthew 9:36–38). Here, Jesus referred to the many souls needing to be brought to repentance and faith as a harvest waiting to be realized.
Jesus used the same metaphor of a spiritual harvest in Samaria. After talking to the woman at the well, Jesus told His disciples, “Don’t you have a saying, ‘It’s still four months until harvest’? I tell you, open your eyes and look at the fields! They are ripe for harvest” (John 4:35). In the days following this statement, many of the Samaritans became believers in Christ (verse 41). Jesus saw the spiritual harvest of souls awaiting in that village.
A spiritual harvest is the result of God’s work in the heart of man. It is clear from the parable of the seed and the sower that some people’s hearts are good soil; when the Word of God is sown there, the person accepts it and continues to mature (Luke 8:9–15). There is nothing we can do to change the soil—that is God’s job (Ezekiel 36:26). However, we can be faithful to sow the seed, help the plants to grow, or reap the harvest. The process of spiritual growth and maturity, from the heart’s regeneration to the recognition of faith, is often a long journey. In fact, the Bible indicates that the sower, the tender, and the reaper are likely to be different people at different times (John 4:35–38; 1 Corinthians 3:6–9).
Just like the physical growth of a field, the spiritual growth of people is a natural, organic process, overseen by God Himself. If we don’t see anyone getting saved, it can be discouraging, but we need to remember that sowing is just as important as reaping. Some of us are sowers and may never see the result of our labor. That is why our focus should be on pleasing the One who sent us into the field rather than on controlling the rate of growth or the amount we reap.
God’s laborers in the spiritual harvest of souls are promised great reward for their faith and perseverance (James 1:12; 1 Peter 5:4; 2 Timothy 4:8; Hebrews 11). This applies to all aspects of our spiritual lives, including witnessing and seeing people saved and growing in the Lord, which is the spiritual harvest we all long to see. Sometimes we don’t see it. Nonetheless, believers are exhorted with these words: “Let us not grow weary of doing good, for in due season we will reap, if we do not give up” (Galatians 6:9) and “A harvest of righteousness is sown in peace by those who make peace” (James 3:18) and “Those who go out weeping, carrying seed to sow, will return with songs of joy, carrying sheaves with them” (Psalm 126:6).
Jesus told us to pray to the Lord of the harvest for more laborers (Matthew 9:38). We should pray about all aspects of the spiritual harvest process, including the preparation of the soil. We can ask God to change people’s hearts. “The Lord’s servant must not be quarrelsome but kind to everyone, able to teach, patiently enduring evil, correcting his opponents with gentleness. God may perhaps grant them repentance leading to a knowledge of the truth” (2 Timothy 2:24–25). God will use us in His fields, each according to our gifts and the need of the moment, as we trust Him.
Personal evangelism is the act of a person sharing the gospel with another. There are many different methods of personal evangelism, and it is a hot topic within Christianity. Books, classes, and seminars are dedicated to the subject of witnessing, soul-winning, and helping others find salvation through faith in Jesus Christ. Not every method is effective or biblically supportable; according to Bible teacher Dr. John MacArthur, “Jesus would have failed personal evangelism class in almost every Bible college and seminary I know.”
According to a 2016 Barna survey, 73 percent of Americans claim to be Christians. However, after applying scriptural tests to those claims, only around 31 percent actually qualify as practicing Christians. The Bible knows no other kind (Matthew 7:19–21; 1 John 3:7–10). Clearly, what has passed for personal evangelism for the last several generations has not been effective.
When Jesus practiced “personal evangelism,” He often seemed to make it more difficult for those who showed interest (Luke 9:57–62). His encounter with the rich young ruler in Matthew 19:16–24 is a good example of showing an unbeliever what true discipleship costs, but this type of personal evangelism is rare today. Jesus was not interested in what has come to be known as “easy believism.” Some modern methods of personal evangelism are so mechanical that salvation is presented almost as a business arrangement: “Plug in this sinner’s prayer and voilà! Eternal life!” This presentation may result in many responses, but is that real salvation? The Barna statistics indicate otherwise.
Paul exemplified effective personal evangelism. After his radical conversion to Christ (Acts 9), Paul’s entire life changed. His new life motto was encapsulated in these words from Galatians 2:20: “I have been crucified with Christ and I no longer live, but Christ lives in me. The life I now live in the body, I live by faith in the Son of God, who loved me and gave himself for me.” Paul lived evangelism. Everything he did was for the glory of God (1 Corinthians 10:31). He sought ways to impart truth everywhere he went, in every cultural context (1 Corinthians 9:20–22). The other apostles practiced personal evangelism in the same way. At times, they gained massive responses, and churches were started on the spot (Acts 9:35, 42; 11:24). Other times, the first Christians were mocked, beaten, jailed, or run out of town (2 Corinthians 11:23–28; Acts 16:22–23). So even the best methods of personal evangelism won’t always produce converts.
We can learn a lot about personal evangelism from those first Christians. The following are some factors that contribute to effective personal evangelism:
Prayer. Beautiful words and impassioned speeches may move a soul, but they cannot transform a hard heart. Only the power of the Holy Spirit can bring conviction and repentance (2 Timothy 2:25). The first Christians relied on massive amounts of prayer before they attempted to do anything for the Lord, and God blessed their efforts (Acts 1:14; 4:31; 6:6; 13:3; Colossians 4:4). When our prayer lives are consistent and meaningful, we are ready to engage in personal evangelism.
Biblical knowledge. We don’t have to possess a seminary degree or the ability to read ancient Greek, but we do need an overall understanding of what the Bible says. Many people allow this factor to silence them, citing their lack of biblical knowledge as a reason they don’t witness for Christ. But there is no reason that we cannot study and learn for ourselves what God says about His plan of salvation. Christians should be experts on the gospel. Second Timothy 2:15 commands us to study as unto God so that we will become “as one approved, a worker who does not need to be ashamed and who correctly handles the word of truth.” We need to know the basic truths of Scripture in order to have effective personal evangelism.
A story. We all have a story. If we’ve come to know Christ and have experienced forgiveness of sin and His transforming power in our lives, then we have a story to tell. Effective personal evangelism often incorporates a personal testimony. Paul often recounted his own conversion story in his evangelism, reminding his audience of how wicked he had been and how far God’s grace had brought him (Philippians 3:4–6; Acts 26:9–23; 1 Corinthians 15:9). An example of how a story affects personal evangelism is found in John 9. Jesus healed a man born blind. The Pharisees plied the healed man with questions about Jesus that he could not answer. Finally, in frustration, the man cried out, “Whether he is a sinner or not, I don’t know. One thing I do know. I was blind but now I see!” (verse 25). We may not know the answers to every question we are asked, but we do know what Jesus has done for us. We know that once we were blind to spiritual truths, and now we see.
The right attitude. Much damage has been done in the name of Christ by people trying to conduct personal evangelism without love and without humility. First Corinthians 13:1–3 reminds us that we may do any number of noble-looking deeds, but if we don’t do them in love, we have accomplished nothing. Love for Christ must be first (Mark 12:30), followed closely by a love for people. Our motivation in personal evangelism must never be anger, a desire to condemn someone, or a need to win an argument. We should check our own hearts before embarking on a quest to evangelize others (Matthew 7:3–5). We don’t have to be perfect, but we need to be certain that our desire is the salvation of the lost, not the motivation to look spiritual or to be right. Galatians 5:22–23 is a list of character qualities that will be a part of effective personal evangelism.
Obedience, not results. It is often tempting to scale down biblical truth in personal evangelism in order to elicit the response we desire. But to do so only undermines the work God wants to do in that person’s life. Scripture is replete with examples of people obeying God’s commands, even though the results were nothing like they assumed: Abraham followed God to Canaan—and a famine hit right away (Genesis 12:10). Mary accepted the role of mother to the promised Messiah—then watched Him be mocked and crucified (Luke 1:38; John 19:25). Paul followed the Holy Spirit’s leading to Philippi—and was arrested and imprisoned (Acts 16:6–24).
In our personal evangelism, it is good to remember that we are only responsible to God for our obedience, not the results of that obedience. We may present the gospel thoroughly and lovingly, and the person to whom we witness may hear and understand but choose to walk away. We are not responsible for that reaction, only the level of obedience involved in our presentation. Jesus explained in Luke 8:5–15 that human hearts are like types of soil. The seed sown is the same in each case, but people receive the Word of God differently and respond differently. Our job, as the sowers of seeds, is to present truth as effectively as we know how and entrust the results to God.
Personal evangelism is the responsibility of every believer. God calls each of us to different tasks and endows us with different gifts, but the goal is the same—the salvation of the lost (1 Corinthians 12:6–7; Luke 19:10). He places us in strategic positions for influence, not privilege. We have neighbors, coworkers, friends, and relatives who need to hear the good news about Jesus. Whether we’re called to lead evangelistic crusades or simply cultivate a relationship with an unsaved neighbor, personal evangelism should be the driving force in our lives. Jesus’ words spoken to His disciples more than two thousand years ago still apply to His followers today: “As long as it is day, we must do the works of him who sent me. Night is coming, when no one can work” (John 9:4). As long as we have breath, we can do personal evangelism. As long as we stay surrendered to the Holy Spirit, He will do it through us (Luke 12:12).
Promoters of the false “prosperity gospel” and Word of Faith movement often like to talk about “seeding,” “seed faith offerings,” and “hundred-fold returns.” A seed faith offering is money given in faith that God will multiply it and return it to the giver. The more money you give—and the more faith you have—the more money you get in return. Prosperity preachers often solicit gifts to their ministries by promising such in-kind returns: “Send me $10 and trust God to give you back $1,000.” They give their appeals for money a spiritual gloss with statements such as “God wants to bless you with a miracle” and “Jesus is bigger than your debt.” And they will misuse verses such as Mark 4:8, “Still other seed fell on good soil. It came up, grew and produced a crop, some multiplying thirty, some sixty, some a hundred times.” It’s good to remember the “seed” in this verse is the Word of God (Mark 4:14), not money.
The late Oral Roberts was highly influential in spreading the concept of seed faith offerings, and he taught people to expect a miracle when they sow a “seed” from their “need.” He wrote, “To realize your potential, to overcome life’s problems, to see your life become fruitful, multiply and provide abundance (i.e., health, prosperity, spiritual renewal, in the family or oneself), you should decide to follow the divine law of the sower and the harvest. Sow the seed of His promise in the ground of your need” (from “Principles of the Seed”). In the July 1980 edition of Abundant Life, Roberts wrote, “Solve your money needs with money seeds” (page 4).
Richard Roberts, Oral’s son, says on his website, “Give God something to work with. No matter how little you think you have, sow it in joy and faith, knowing in your heart that you are sowing seed so you may reap miracles. Then start expecting all kinds of miracles!” In May 2016, Roberts’ newsletter appealed for monetary gifts with this statement: “Sow a special $100 seed. . . . If you will plant this seed out of your need and go into a holy agreement with me, then TOGETHER you and I will EXPECT A MIGHTY MIRACLE FROM GOD” (from his website, emphasis in the original).
According to Oral Roberts, the way to take advantage of the law of sowing and reaping is three-fold: 1) look to God as your source, 2) give first so that it may be given to you, and 3) expect a miracle. As a “proof text” for the second step, seed-faith teachers like to use Luke 6:38, “Give, and it will be given to you. A good measure, pressed down, shaken together and running over, will be poured into your lap. For with the measure you use, it will be measured to you.” The misuse of this verse starts with its application to material gain—Jesus was speaking of forgiveness in Luke 6:37, not money. Also, there’s a difference between “Give, and” and “Give so that.” Seed-faith teachers advocate a selfish motive for giving—give so that you can get—and they state as much. The Bible teaches that we give for the sake of benefiting others and to glorify the Lord, not in order to enrich ourselves.
Teachers of seed faith offering also like Matthew 17:20, “Truly I tell you, if you have faith as small as a mustard seed, you can say to this mountain, ‘Move from here to there,’ and it will move. Nothing will be impossible for you.” Of course, this verse says nothing about getting money or making seed faith offerings.
Another passage misused by seed-faith preachers is Mark 10:29–30, “Truly I tell you . . . no one who has left home or brothers or sisters or mother or father or children or fields for me and the gospel will fail to receive a hundred times as much in this present age: homes, brothers, sisters, mothers, children and fields.” Seed-faith teachers latch on to the promise of a “hundred times as much,” but they only apply it to “homes” and “fields”—that is, material wealth. They ignore the rest of the list. Are we to suppose that Jesus promised His followers a hundred literal mothers or that we should expect a hundred times more blood relatives than we have now? Or was Jesus speaking of an increased spiritual family? Since the mothers and fathers and brothers and sisters are spiritual, then perhaps the homes and fields are spiritual, as well.
The promoters of the doctrine of seed faith offerings ignore several important details in Scripture. Consider, for example, 2 Corinthians 9:10–12, “He who supplies seed to the sower and bread for food will also supply and increase your store of seed and will enlarge the harvest of your righteousness. You will be enriched in every way so that you can be generous on every occasion, and through us your generosity will result in thanksgiving to God. This service that you perform is not only supplying the needs of the Lord’s people but is also overflowing in many expressions of thanks to God.” This passage says God supplies the seed for sowing; that is, He supplies the resources for us to generously give away. And, when we give, God will supply more resources so the giving continues. Note, however, the reaping is not monetary gain but “the harvest of your righteousness.” Also, it is thanksgivings to God that overflow, not our bank accounts. The seed sown in this passage does not result in miracles or in personal wealth.
The promoters of seed faith offerings also ignore the fact that the apostles were not wealthy men. The apostles certainly gave to others: “I will very gladly spend for you everything I have and expend myself as well” (2 Corinthians 12:15). Based on the doctrine of seed faith offerings, Paul should have been a rich man. Yet, “to this very hour we go hungry and thirsty, we are in rags, we are brutally treated, we are homeless. We work hard with our own hands” (1 Corinthians 4:10–11). The apostles were materially poor, yet they were spiritually blessed by the Lord.
God loves a cheerful giver (2 Corinthians 9:7), but we must not assume that His favor will be shown in financial returns. Nor should we appropriate promises given to Old Testament Israel for ourselves. Our motive for giving should not be to get money in return. Our goal should be godliness with contentment (see 1 Timothy 6:6–10). We should pray, “Lord, help me learn to be content with what I have, even if I am hungry or in need” (see Philippians 4:11–13).
The seed faith teaching amounts to little more than a get-rich-quick scheme that preys upon the desperate and hurting among God’s people. Peter warned the church about such chicanery: “Through covetousness shall they with feigned words make merchandise of you” (2 Peter 2:3, KJV).
The question “who are the seed of Abraham?” can be answered several ways, and it is important to make some distinctions. There is the Seed of Abraham (Seed being singular); there is the seed of Abraham physically (descendants of Abraham according to the flesh); and there is the seed of Abraham spiritually(those who, like Abraham, have faith in God).
The (singular) Seed of Abraham is Christ, as Galatians 3:16, quoting Genesis 12:7, says, “The promises were spoken to Abraham and to his seed. Scripture does not say ‘and to seeds,’ meaning many people, but ‘and to your seed,’ meaning one person, who is Christ.” The passage goes on to explain that an inheritance was promised to Abraham’s Seed (Christ) apart from the Law. Later, the Mosaic Law was introduced, but it did not annul the promises made to Abraham or to Abraham’s Seed (Christ).
Just as Abraham believed God and his faith was counted as righteousness (Genesis 15:6), so are all today who believe in God’s Son justified apart from the Law. In this way, Abraham is the “father” of all who believe (Romans 4:11–17). “If you belong to Christ, then you are Abraham’s seed, and heirs according to the promise” (Galatians 3:29).
Of course, the seed of Abraham can also refer to the Hebrew people who descended from Abraham through Isaac. Still more broadly, the seed of Abraham could include Arabs, who trace their lineage through Ishmael. This is the physical seed of Abraham. The spiritual seed of Abraham (believers in Jesus Christ) is comprised of people of all nationalities and ethnicities.
The Jewish religious leaders of the first century took pride in that they were Abraham’s seed. They saw their physical connection to Abraham as a guarantee of God’s favor. This attitude kept them from seeing their need for repentance of the heart—and brought condemnation from John the Baptist, who warned them to repent. Anticipating their fallback argument that they were the seed of Abraham, John said, “Do not think you can say to yourselves, ‘We have Abraham as our father.’ I tell you that out of these stones God can raise up children for Abraham” (Matthew 3:9).
Jesus dealt with the same issue later. In speaking to the unbelieving Jews, Jesus emphasized their need to receive His words as truth and obey His commands. They replied, “We be Abraham’s seed” (John 8:33, KJV). Jesus then rebukes them for plotting ways to murder Him; their stubborn response was again, “Abraham is our father” (verse 39a). At this, Jesus makes a distinction between the physical seed of Abraham and the true, spiritual seed of Abraham: “If you were Abraham’s children . . . then you would do what Abraham did” (verse 39b). The conversation heats up as the Jews for a third time reference their connection to Abraham: “Are you greater than our father Abraham?” they ask Jesus (verse 53). Jesus provokes them further: “Your father Abraham rejoiced at the thought of seeing my day; he saw it and was glad” (verse 56). The Jews’ are incredulous that Jesus would claim to be a contemporary of Abraham, and that’s when Jesus brings the exchange to a climax with a claim to full deity: “Very truly I tell you, . . . before Abraham was born, I am!” (verse 58). In a fury, the Jews attempted to stone Jesus (verse 59), again proving that being the physical seed of Abraham is not enough—they had to be born again (John 3:3).
Paul sums up the difference between the seeds of Abraham in Romans 2:28–29: “A person is not a Jew who is one only outwardly, nor is circumcision merely outward and physical. No, a person is a Jew who is one inwardly; and circumcision is circumcision of the heart, by the Spirit, not by the written code. Such a person’s praise is not from other people, but from God.”
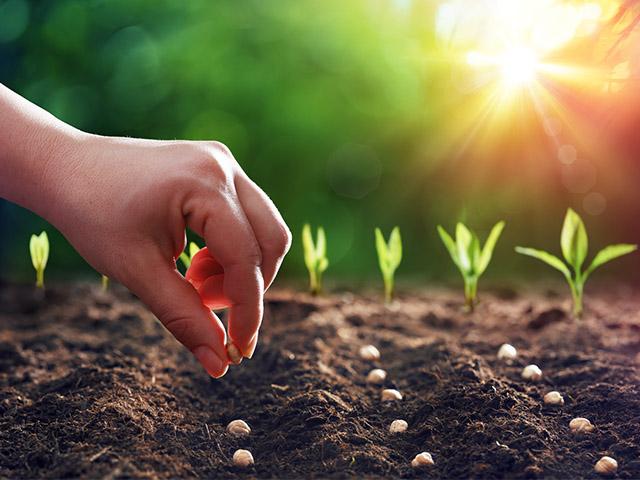
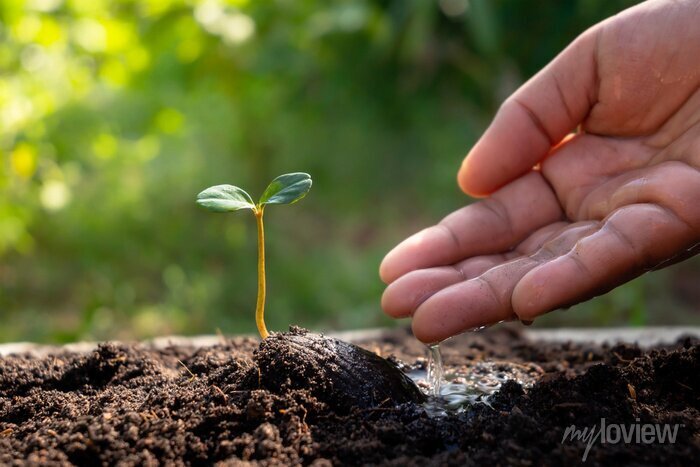
The first thing we notice about this parable is its similarity to the Parable of the Sower in Mark 4:2-9. In some ways, this parable expands on Jesus’ teaching of how the “good soil” (a receptive heart) receives the “seed” (the Word of God).
In the Parable of the Growing Seed, Jesus tells of a man who scatters seed on the ground and then allows nature to take its course. As the man who sowed the seed goes about his business day by day, the seed begins to have an effect. First, the seed sprouts; then it produces a stalk and leaves, then a head of grain, and, finally, fully developed kernels in the head. Jesus emphasizes that all of this happens without the man’s help. The man who scattered the seed cannot even fully understand how it happens—it is simply the work of nature. “All by itself the soil produces” (verse 28).
The parable ends with a harvest. As soon as the grain is ripe, the sickle is employed, and the seed is harvested. This happens at just the right time.
Jesus did not explain this parable, as He did some others. Instead, He left it to us to understand its meaning. Taking the seed to be the Word of God, as in Mark 4:14, we can interpret the growth of the plants as the working of God’s Word in individual hearts. The fact that the crop grows without the farmer’s intervention means that God can accomplish His purposes even when we are absent or unaware of what He’s doing. The goal is the ripened grain. At the proper time, the Word will bring forth its fruit, and the Lord of the harvest (Luke 10:2) will be glorified.
The truth of this parable is well illustrated in the growth of the early church: “I planted the seed, Apollos watered it, but God made it grow” (1 Corinthians 3:6). Just like a farmer cannot force a crop to grow, an evangelist cannot force spiritual life or growth on others.
To summarize the point of the Parable of the Growing Seed: “The way God uses His Word in the heart of an individual is mysterious and completely independent of human effort.” May we be faithful in “sowing the seed,” praying for a harvest, and leaving the results to the Lord!
Faith is so vital to the Christian life that Scripture tells us that, without it, it is impossible to please God (Hebrews 11:6). Yet faith is such a powerful gift from God (Ephesians 2:8–9) Christ told His disciples that, with just a tiny measure of it, the size of a mustard seed, they could move mountains. So, what does it mean to have “mustard seed faith”?
We see the reference to “mustard seed faith” twice in Scripture. First, in Matthew 17:14–20, we see Christ’s disciples unable to exorcise a demon from a young boy, even though Jesus had previously given them the authority to do this very thing (Matthew 10:1). When they inquired of Jesus why they were not able to drive the demon out, the Master replied, “Because you have so little faith. I tell you the truth, if you have faith as small as a mustard seed, you can say to this mountain, ‘move from here to there’ and it will move; Nothing will be impossible for you” (Matthew 17:14–20). Next, in Luke 17:6, Jesus tells His disciples, “If you have faith as small as a mustard seed, you can say to this mulberry tree, ‘Be uprooted and planted in the sea,’ and it will obey you.” By using the uncommonly small mustard seed as an example, Jesus is speaking figuratively about the incalculable power of God when unleashed in the lives of those with true faith.
We know that this statement about moving mountains and uprooting trees by faith is not to be taken literally. The key to understanding the passages is the nature of faith, which is a gift from God. The power of faith reflects the omnipotent nature of the God who bestows faith on His own. The mustard seed is one of the tiniest seeds found in the Middle East, so the conclusion is that the amount of faith needed to do great things is very small indeed. Just as in the parable of the mustard seed (Matthew 13:31–32), Jesus uses rhetorical hyperbole to make the point that little is much when it comes from God. The mustard seed in the parable grows to be a huge tree, representing the tiny beginnings of Christianity when just a few disciples began to preach and teach the gospel. Eventually, the kingdom grew to huge proportions, encompassing the entire world and spreading over centuries.
So, too, does the tiniest bit of faith, when it is true faith from God, grow to immense proportions in the lives of believers and spreading out to influence all they come into contact with. One has only to read histories of the great men of the faith, such as Foxe’s Book of Martyrs, to know that superhuman feats were performed by those whose faith was, at one time, only the size of a mustard seed.
The story of the wise man who built his house upon a rock is found in Matthew 7:24–27. It is one of the parables of Jesus. During His Sermon on the Mount, Jesus told a story about two men: one who built his house upon a rock and another who built his house upon sand. The house built upon a rock weathered the storm, and the builder is called wise; but the house built on the sand collapsed during the storm, and the builder is called foolish.
The meaning of this parable is quite obvious: proper foundations are necessary. With a literal house, it is unwise to build on sand, because the foundation will be unsteady and the house will eventually suffer some kind of damage. This will waste resources, and all the time and work put into building the house in the first place will have gone for nothing. In contrast, it is wise to build one’s house on a sure foundation; anchoring to bedrock makes a building withstand the test.
But Jesus’ sermon was not concerned with house construction or building code violations. The spiritual meaning of the parable is found in Matthew 7:24: “Everyone who hears these words of mine and puts them into practice is like a wise man who built his house on the rock.” We are each building a life. The proper foundation for a life is Jesus’ words—not just the hearing of them, but the doing of them, too (see James 1:22).
It seems at times that everything in the world is set up to make us turn away from God’s words. And often, our own feelings pull us toward doing the exact opposite of what the Bible says. But a wise man will follow the words of God despite these pressures—not as a way to “show off” or earn salvation, but because he trusts God. All through the Sermon on the Mount, Jesus presented Himself as the final authority on and fulfiller of the Law; He ends the sermon with a call to heed His message and, in fact, find one’s security in Him (see 1 Corinthians 3:11).
As we follow the Lord, learning to trust and obey Him, we receive a reward: our “house” is steady and solid, unshaken by circumstances. The wise man is the believer whose life is built upon the Rock of Christ; in this world he has faith and hope, and in the next everlasting life and love (see 1 Corinthians 13:13). The wise man is like the tree planted by the riverside, whose leaf does not wither (Psalm 1:1–3).
A parable is, literally, something “cast alongside” something else. Jesus’ parables were stories that were “cast alongside” a truth in order to illustrate that truth. His parables were teaching aids and can be thought of as extended analogies or inspired comparisons. A common description of a parable is that it is an earthly story with a heavenly meaning.
For a time in His ministry, Jesus relied heavily on parables. He told many of them; in fact, according to Mark 4:34a, “He did not say anything to them without using a parable.” There are about 35 of Jesus’ parables recorded in the Synoptic Gospels.
It had not always been that way. In the early part of His ministry, Jesus had not used parables. Suddenly, He begins telling parables exclusively, much to the surprise of His disciples, who asked Him, “Why do you speak to the people in parables?” (Matthew 13:10).
Jesus explained that His use of parables had a two-fold purpose: to reveal the truth to those who wanted to know it and to conceal the truth from those who were indifferent. In the previous chapter (Matthew 12), the Pharisees had publicly rejected their Messiah and blasphemed the Holy Spirit (Matthew 12:22–32). They fulfilled Isaiah’s prophecy of a hardhearted, spiritually blind people (Isaiah 6:9–10). Jesus’ response was to begin teaching in parables. Those who, like the Pharisees, had a preconceived bias against the Lord’s teaching would dismiss the parables as irrelevant nonsense. However, those who truly sought the truth would understand.
Jesus made sure His disciples understood the meaning of the parables: “When he was alone with his own disciples, he explained everything” (Mark 4:34b).
Interpreting a parable can present some challenges for the student of the Bible. Sometimes, interpretation is easy because the Lord Himself gave the interpretation—the Parable of the Sower and the Parable of the Wheat and the Tares are both explained in Matthew 13. Here are some principles that help in interpreting the other parables:
1) Determine the scope of the spiritual truth being presented. Sometimes, a parable is preceded by some introductory words that provide a context. For example, often Jesus preceded a parable with the words “this is what the kingdom of heaven is like.” Also, before the Parable of the Pharisee and the Tax Collector, we read this: “To some who were confident of their own righteousness and looked down on everyone else, Jesus told this parable” (Luke 18:9). This introduction delineates the subject matter being illustrated (self-righteousness and spiritual pride).
2) Distinguish between the “meat” of the story and what is just ornamentation. In other words, not every detail of a parable carries a deep spiritual meaning. Some details are simply there to help the story seem more realistic. For example, in Jesus’ own interpretation of the Parable of the Sower, He does not comment on the fact that there are four (and only four) different types of soil. That detail was meaningless to the overall point Jesus was making.
3) Compare Scripture with Scripture. This basic principle of hermeneutics is invaluable when studying parables. Jesus’ parables will never contradict the rest of the Word of God, which He came to express (John 12:49). The parables are meant to illustrate doctrine, and the teachings Jesus illuminated are found clearly taught elsewhere in the Bible.
There are parables in the Bible other than those found in the Gospels. The book of Proverbs is full of analogies—whenever Solomon used a comparison to teach a truth, especially in emblematic parallelism, the result was a simple parable. For example, Proverbs 20:2 says, “A king’s wrath strikes terror like the roar of a lion.” The roaring of a lion is “cast alongside” the wrath of a king for the purpose of comparison. That is the essence of parabolic language.
After telling some of His parables, Jesus said, “Whoever has ears to hear, let them hear” (Mark 4:9, 23). This was a call to listen to the parables, not just as one would listen to an ordinary story but as one who is seeking the truth of God. May God grant us all ears to truly “hear.”
The Parable of the Weeds Explained
36 Then he left the crowds and went into ithe house. And his disciples came to him, saying, j“Explain to us the parable of the weeds of the field.” 37 He answered, “The one who sows the goodseed is the Son of Man. 38 The field is the world, and the good seed iskthe sons of the kingdom. The weeds are lthe sons of the evil one, 39 and the enemy who sowed them is the devil. mThe harvest is ntheend of the age, and the reapers are angels. 40 Just as the weeds oaregathered and burned with fire, so will it be at nthe end of the age. 41 pThe Son of Man will send his angels, and they will gather out ofhis kingdom all qcauses of sin and rall law-breakers, 42 sand throwthem into the fiery furnace. In that place tthere will be weeping andgnashing of teeth. 43 Then uthe righteous will shine like the sun vinthe kingdom of their Father. wHe who has ears, let him hear.
The Parable of the Wheat and the Weeds, or Tares, is filled with spiritual significance and truth. But, in spite of the clear explanation of the parable that Jesus gave (Matthew 13:36-43), this parable is very often misinterpreted. Many commentaries and sermons have attempted to use this story as an illustration of the condition of the church, noting that there are both true believers (the wheat) and false professors (the weeds) in both the church at large and individual local churches. While this may be true, Jesus distinctly explains that the field is not the church; it is the world (v. 38).
Even if He hadn’t specifically told us the world is the setting of the story, it would still be obvious. The landowner tells the servants not to pull up the weeds in the field, but to leave them until the end of the age. If the field were the church, this command would directly contradict Jesus’ teaching in Matthew 18, which tells us how to deal with unrepentant sinners in the church: they are to be put out of the fellowship and treated as unbelievers. Jesus never instructed us to let impenitent sinners remain in our midst until the end of the age. So, Jesus is teaching here about “the kingdom of heaven” (v. 24) in the world.
In the agricultural society of Christ’s time, many farmers depended on the quality of their crops. An enemy sowing weeds would have sabotaged a business. The tares in the parable were likely darnel because that weed, until mature, appears as wheat. Without modern weed killers, what would a wise farmer do in such a dilemma? Instead of tearing out the wheat with the tares, the landowner in this parable wisely waited until the harvest. After harvesting the whole field, the tares could be separated and burned. The wheat would be saved in the barn.
In the explanation of parable, Christ declares that He Himself is the sower. He spreads His redeemed seed, true believers, in the field of the world. Through His grace, these Christians bear the fruit of the Spirit (Galatians 5:22-24). Their presence on earth is the reason the “kingdom of heaven” is like the field of the world. When Jesus said, “The kingdom of heaven is at hand” (Matthew 3:2; 4:17), He meant the spiritual realm which exists on earth side by side with the realm of the evil one (1 John 5:19). When the kingdom of heaven comes to its fruition, heaven will be a reality and there will be no “weeds” among the “wheat.” But for now, both good and bad seeds mature in the world.
The enemy in the parable is Satan. In opposition to Jesus Christ, the devil tries to destroy Christ’s work by placing false believers and teachers in the world who lead many astray. One has only to look at the latest televangelist scandal to know the world is filled with professing “Christians” whose ungodly actions bring reproach on the name of Christ. But we are not to pursue such people in an effort to destroy them. For one thing, we don’t know if immature and innocent believers might be injured by our efforts. Further, one has only to look at the Spanish Inquisition, the Crusades, and the reign of “Bloody Mary” in England to see the results of men taking upon themselves the responsibility of separating true believers from false, a task reserved for God alone. Instead of requiring these false believers to be rooted out of the world, and possibly hurting immature believers in the process, Christ allows them to remain until His return. At that time, angels will separate the true from false believers.
In addition, we are not to take it upon ourselves to uproot unbelievers because the difference between true and false believers isn’t always obvious. Tares, especially in the early stages of growth, resemble wheat. Likewise, a false believer may resemble a true believer. In Matthew 7:22, Jesus warned that many profess faith but do not know Him. Thus, each person should examine his own relationship with Christ (2 Corinthians 13:5). First John is an excellent test of salvation.
Jesus Christ will one day establish true righteousness. After He raptures the true church out of this world, God will pour out His righteous wrath on the world. During that tribulation, He will draw others to saving faith in Jesus Christ. At the end of the tribulation, all unbelievers will be judged for their sin and unbelief; then, they will be removed from God’s presence. True followers of Christ will reign with Him. What a glorious hope for the “wheat”!
Who Is the Greatest?
18 tAt that time the disciples came to Jesus, saying, “Who is the greatest in the kingdom of heaven?” 2 And calling to him a child, he put him in the midst of them 3 and said, “Truly, I say to you, unlessyou uturn and vbecome like children, you wwill never enter thekingdom of heaven. 4 xWhoever humbles himself like this child is thewgreatest in the kingdom of heaven.
5 y“Whoever receives one such child in my name receives me, 6 butzwhoever causes one of these alittle ones who believe in me to sin,1 itwould be better for him to have a great millstone fastened around hisneck and to be drowned in the depth of the sea.
Galatians 5:22–24But the fruit of the Spirit is love, joy, peace, forbearance, kindness, goodness, faithfulness, 23 gentleness and self-control. Against such things there is no law. 24 Those who belong to Christ Jesus have crucified the flesh with its passions and desires.
The debate rages over whether “the rock” on which Christ will build His church is Peter, or Peter’s confession that Jesus is “the Christ, the Son of the Living God” (Matthew 16:16). In all honesty, there is no way for us to be 100% sure which view is correct. The grammatical construction allows for either view. The first view is that Jesus was declaring that Peter would be the “rock” on which He would build His church. Jesus appears to be using a play on words. “You are Peter (petros) and on this rock (petra) I will build my church.” Since Peter’s name means rock, and Jesus is going to build His church on a rock – it appears that Christ is linking the two together. God used Peter greatly in the foundation of the church. It was Peter who first proclaimed the Gospel on the day of Pentecost (Acts 2:14-47). Peter was also the first to take the Gospel to the Gentiles (Acts 10:1-48). In a sense, Peter was the rock “foundation” of the church.
The other popular interpretation of the rock is that Jesus was referring not to Peter, but to Peter’s confession of faith in verse 16: “You are the Christ, the son of the living God.” Jesus had never explicitly taught Peter and the other disciples the fullness of His identity, and He recognized that God had sovereignly opened Peter’s eyes and revealed to him who Jesus really was. His confession of Christ as Messiah poured forth from him, a heartfelt declaration of Peter’s personal faith in Jesus. It is this personal faith in Christ which is the hallmark of the true Christian. Those who have placed their faith in Christ, as Peter did, are the church. Peter expresses this in 1 Peter 2:4 when he addressed the believers who had been dispersed around the ancient world: “Coming to Him as to a living stone, rejected indeed by men, but chosen by God and precious, you also, as living stones, are being built up a spiritual house, a holy priesthood, to offer up spiritual sacrifices acceptable to God through Jesus Christ.”
At this point, Jesus declares that God had revealed this truth to Peter. The word for “Peter,” Petros, means a small stone (John 1:42). Jesus used a play on words here with petra (“on this rock”) which means a foundation boulder, as in Matthew 7:24, 25 when He described the rock upon which the wise man builds his house. Peter himself uses the same imagery in his first epistle: the church is built of numerous small petros “living stones” (1 Peter 2:5) who, like Peter, confess that Jesus is the Christ, the Son of the living God, and those confessions of faith are the bedrock of the church.
In addition, the New Testament makes it abundantly clear that Christ is both the foundation (Acts 4:11, 12; 1 Corinthians 3:11) and the head (Ephesians 5:23) of the church. It is a mistake to think that here He is giving either of those roles to Peter. There is a sense in which the apostles played a foundational role in the building of the church (Ephesians 2:20), but the role of primacy is reserved for Christ alone, not assigned to Peter. So, Jesus’ words here are best interpreted as a simple play on words in that a boulder-like truth came from the mouth of one who was called a small stone. And Christ Himself is called the “chief cornerstone” (1 Peter 2:6, 7). The chief cornerstone of any building was that upon which the building was anchored. If Christ declared Himself to be the cornerstone, how could Peter be the rock upon which the church was built? It is more likely that the believers, of which Peter is one, are the stones which make up the church, anchored upon the Cornerstone, “and he who believes on Him will by no means be put to shame” (1 Peter 2:6).
The Roman Catholic Church uses the argument that Peter is the rock to which Jesus referred as evidence that it is the one true church. As we have seen, Peter’s being the rock is not the only valid interpretation of this verse. Even if Peter is the rock in Matthew 16:18, this is meaningless in giving the Roman Catholic Church any authority. Scripture nowhere records Peter being in Rome. Scripture nowhere describes Peter as being supreme over the other apostles. The New Testament does not describe Peter as being the “all authoritative leader” of the early Christian church. Peter was not the first pope, and Peter did not start the Roman Catholic Church. The origin of the Catholic Church is not in the teachings of Peter or any other apostle. If Peter truly was the founder of the Roman Catholic Church, it would be in full agreement with what Peter taught (Acts chapter 2, 1 Peter, 2 Peter).
Since ancient times, builders have used cornerstones in their construction projects. A cornerstone was the principal stone, usually placed at the corner of an edifice, to guide the workers in their course. The cornerstone was usually one of the largest, the most solid, and the most carefully constructed of any in the edifice. The Bible describes Jesus as the cornerstone that His church would be built upon. He is foundational. Once the cornerstone was set, it became the basis for determining every measurement in the remaining construction; everything was aligned to it. As the cornerstone of the building of the church, Jesus is our standard of measure and alignment.
The book of Isaiah has many references to the Messiah to come. In several places the Messiah is referred to as “the cornerstone,” such as in this prophecy: “So this is what the sovereign Lord says: ‘See, I lay a stone in Zion, a tested stone, a precious cornerstone for a sure foundation; the one who trusts will never be dismayed. I will make justice the measuring line and righteousness the plumb line’” (Isaiah 28:16–17). In context, God speaks to the scoffers and boasters of Judah, and He promises to send the cornerstone—His precious Son—who will provide the firm foundation for their lives, if they would but trust in Him.
In the New Testament, the cornerstone metaphor is continued. The apostle Paul desires for the Ephesian Christians to know Christ better: “Consequently, you are no longer foreigners and aliens, but fellow citizens with God’s people and members of God’s household, built on the foundation of the apostles and prophets, with Christ Jesus himself as the chief cornerstone. In him the whole building is joined together and rises to become a holy temple in the Lord” (Ephesians 2:19– 21). Furthermore, in 1 Peter 2:6, what Isaiah said centuries before is affirmed in exactly the same words.
Peter says that Jesus, as our cornerstone, is “chosen by God and precious to him” (1 Peter 2:4). The Cornerstone is also reliable, and “the one who trusts in him will never be put to shame” (verse 6).
Unfortunately, not everyone aligns with the cornerstone. Some accept Christ; some reject Him. Jesus is the “stone the builders rejected” (Mark 12:10; cf. Psalm 118:22). When news of the Messiah’s arrival came to the magi in the East, they determined to bring Him gold, frankincense, and myrrh. But when that same news came to King Herod in Jerusalem, his response was to attempt to kill Him. From the very beginning, Jesus was “a stone that causes people to stumble and a rock that makes them fall” (1 Peter 2:8).
How can people reject God’s chosen, precious cornerstone? Simply put, they want to build something different from what God is building. Just as the people building the tower of Babel rebelled against God and pursued their own project, those who reject Christ disregard God’s plan in favor of their own. Judgment is promised to all those who reject Christ: “Anyone who falls on this stone will be broken to pieces; anyone on whom it falls will be crushed” (Matthew 21:44).
The Tower of Babel is described in Genesis 11:1-9. After the Flood, God commanded humanity to "increase in number and fill the earth" (Genesis 9:1). Humanity decided to do the exact opposite, “Then they said, ‘Come, let us build ourselves a city, with a tower that reaches to the heavens, so that we may make a name for ourselves and not be scattered over the face of the whole earth’” (Genesis 11:4). Humanity decided to build a great city and all congregate there. They decided to build a gigantic tower as a symbol of their power, to make a name for themselves (Genesis 11:4). This tower is remembered as the Tower of Babel.
We assume that there were three wise men because of the three gifts that were given: gold, incense, and myrrh (Matthew 2:11). However, the Bible does not say there were only three wise men. There could have been many more. Tradition says that there were three and that their names were Gaspar/Caspar, Melchior, and Balthasar/Balthazar, but since the Bible does not say, we have no way of knowing whether the tradition is accurate.
It is a common misconception that the wise men visited Jesus at the stable on the night of His birth. In fact, the wise men came days, months, or possibly even years later. That is why Matthew 2:11 says the wise men visited and worshiped Jesus in a house, not at the stable.
We know that the magi were wise men from "the East," most likely Persia, or modern-day Iran. This means the wise men traveled 800 to 900 miles to see the Christ child. Most likely, the magi knew of the writings of the prophet Daniel, who in time past had been the chief of the court seers in Persia. Daniel 9:24-27 includes a prophecy which gives a timeline for the birth of the Messiah. Also, the magi may have been aware of the prophecy of Balaam (who was from the town of Pethor on the Euphrates River near Persia) in Numbers 24:17. Balaam’s prophecy specifically mentions a “star coming out of Jacob.”
The wise men were guided to look for the King of the Jews
by a miraculous stellar event, the “Star of Bethlehem,”
which they called “His star” (Matthew 2:2).
They came to Jerusalem and asked concerning the birth of Christ, and they were directed to Bethlehem (Matthew 2:4–8). They followed God’s guidance joyfully (Matthew 2:10).
When they arrived in Bethlehem, they gave costly gifts to Jesus and worshiped Him.
God warned them in a dream against returning to Herod, so, in defiance of the king, they left Judea by another route (Matthew 2:12).
So, the magi were men who
1) read and believed God’s Word,
2) sought Jesus,
3) recognized the worth of Christ,
4) humbled themselves to worship Jesus, and
5) obeyed God rather than man.
They were truly wise men!
In Isaiah’s prophecy about the coming Messiah, he says:
“For a child will be born to us, a son will be given to us;
And the government will rest on His shoulders;
And His name will be called
Wonderful Counselor, Mighty God,
Eternal Father, Prince of Peace”
(Isaiah 9:6).
The one who sits at the
Right hand
of God
The Coming of the Lord
is at Hand




 RSS Feed
RSS Feed